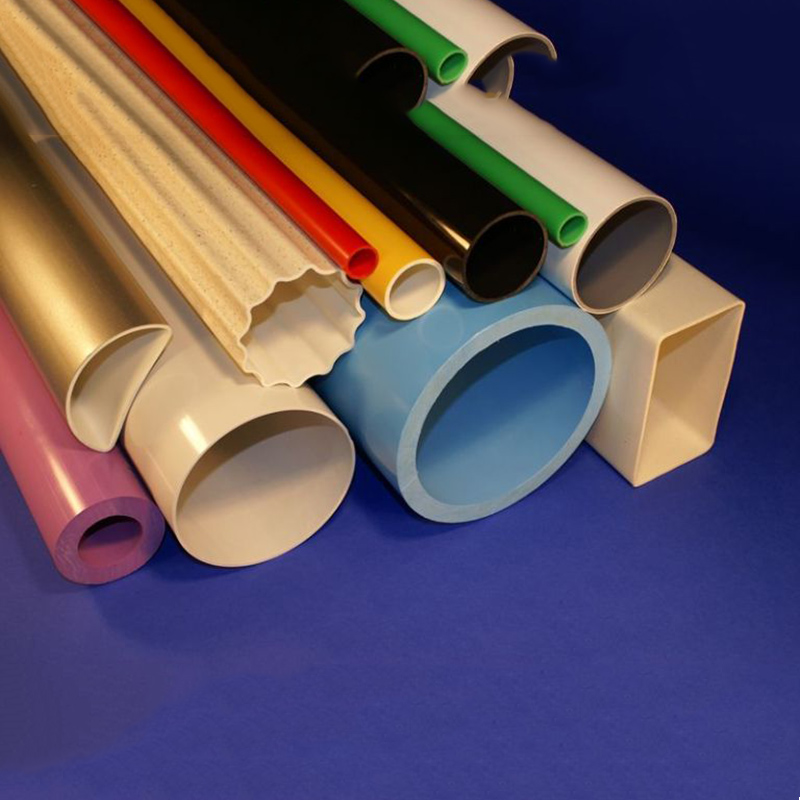
Pvc Suspension Resin
Product Overview
PVC Suspension Resin is a polymer manufactured from vinyl chloride monomer. It is used extensively in building and construction, automotive, and medical industries.
PVC suspension grade production:
We produces PVC Suspension Resin through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer. The monomer,water and suspending agents are fed into a polymerization reactor and are agitated at high speeds to form small droplets of vinyl chloride monomer. After an initiator is added, the vinyl chloride monomer droplets are then polymerized into PVC Suspension Resin under controlled pressures and temperatures. After polymizeration is complete, the resulting slurry is stripped of unreacted vinyl chloride monomer, the excess water is removed, and the resulting solid is dried to form the final product. The final PVC Suspension Resin contains less than 5 parts permillion of residual vinyl chloride monomer.
Many properties of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) make it ideal for a variety of applications. It is biologically and chemically resistant; it is durable and ductile; and it can be made softer and flexible by the addition of plasticizers. With all downstream applications, appropriate registrations and/or approvals may be required. Possible uses for polyvinyl chloride are described below:
Pipes – Roughly half polyvinyl chloride is used to produce pipes for municipal, construction, and industrial applications. It is particularly well suited for this purpose due to its light weight, high strength, low reactivity, and corrosion and bacterial resistance. Additionally, PVC pipes can be fused together in a variety of ways, including solvent cements, adhesives, and heat-fusion, creating permanent joints that are impervious to leakage. Globally, piping is the single largest use for PVC. Residential and Commercial Siding – Rigid PVC is used to make vinyl siding. This material comes in a wide range of colors and finishes and is used as a substitute for wood or metal.
It is also used in window sills and door frames, gutters and downspouts, and double glazing window frames.
Packaging – PVC is widely used as a protecting film in stretch and shrink wrapping, laminate films with polyethylene, rigid blister packaging, and food and film packaging.
It can also be blow molded into bottles and containers. PVC acts as a microbial and water resistant barrier, protecting food, household cleaners, soaps and toiletries. Wiring Insulations – PVC is used as the insulation and fire retardant on electrical wiring. The wires are coated with the resin and the chlorine acts as a free radical scavenger to insulate and reduce the spread of fire. Medical -
PVC is used to make blood and intravenous bags, kidney dialysis and blood transfusion equipment, cardiac catheters, endotracheal tubes, artificial heart valves, and other medical equipment. Automotive – PVC is used to make body side moldings, windshield system components, interior upholstery, dashboards, arm rests, floor mats, wire coatings, abrasion coatings, adhesives, and sealants. Consumer Goods – Both rigid and flexible PVC is used in a wide variety of finished consumer goods, including modern furniture design, air conditioners, refrigerators, phone systems, computers, power tools, electrical cords, garden hoses, clothing, toys, luggage, apparel, vacuums, and credit card stock sheet. PVC can be blended with other plastics to customize the product s properties including color, hardness, abrasion resistance, etc. This method allows producers to determine the customized look and feel of the final product.