Low Density Polyethylene
Low Density Polyethylene,
Low Density Polyethylene,
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a synthetic resin using a high pressure process via free radical polymerization of ethylene and is therefore also called “high-pressure polyethylene”. Since its molecular chain has many long and short branches, LDPE is less crystalline than high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and its density is lower. It features light, flexible, good freezing resistance and impact resistance. LDPE is chemically stable. It has good resistance to acids (except strongly oxidizing acids), alkali, salt, excellent electrical insulation properties. Its vapor penetration rate is low. LDPE has high fluidity and good processability. It is suitable for being used in all types of thermoplastic processing processes, such as injection molding, extrusion molding, blow molding, rotomolding, coating, foaming, thermoforming, hot-jet welding and thermal welding
Application
LDPE is principally used for making films. It is widely used in the production of agricultural film (mulching film and shed film), packaging film (for use in packing candies, vegetables and frozen food), blown film for packaging liquid (for use in packaging milk, soy sauce, juice, bean curds and soy milk), heavy-duty packaging bags, shrinkage packaging film, elastic film, lining film, buildinguse film, general-purpose industrial packaging film and food bags. LDPE is also widely used in the production of wire & cable insulation sheath. Cross-linked LDPE is the main material used in the insulation layer of high-voltage cables. LDPE is also used in the production of injection-molded products (such as artificial flowers, medical instruments, medicine and food packaging material) and extrusion-molded tubes, plates, wire & cable coatings and profiled plastic products. LDPE is also used for making blow-molded hollow products such as containers for holding food, medicine, cosmetics and chemical products, and tanks.
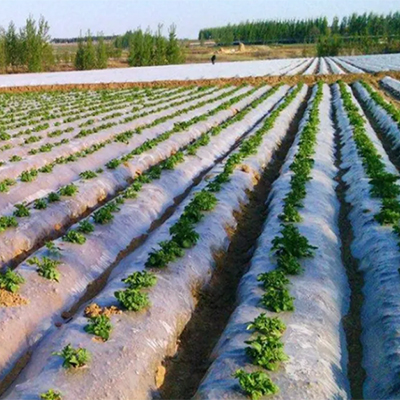






Package, Storage and Transportation

LDPE is an abbreviation for Low Density Polyethylene. Polyethylene is made by polymerization of ethylene. (Poly means ‘a lot’; in fact, it means a lot of ethylene). Ethylene is obtained by cracking a light petroleum derivative such as naphtha.
The low density is obtained by the high-pressure polymerization process. This creates molecules with many side branches. The side branches ensure that the degree of crystallization remains relatively low. In other words, due to their irregular shape, molecules cannot lie in or on top of each other in a well-organized way, so that less of them fit in a certain space. The lower the degree of crystallization, the lower the density of a material.
A good example of this in daily life is water and ice. Ice is water in a (higher) crystallized state, and therefore much lighter than water (melted ice).
LDPE is a kind of thermoplastic. It is a plastic that softens when heated, unlike rubber for example. This makes thermoplastics suitable for reuse. After heating, it can be brought into other desired shapes.